Response to Climate Change
Mid- to long-term climate change response strategies and objectives
Hyosung Chemical is a global company that focuses on businesses with a significant impact on climate change. We make various efforts throughout our management to reduce this impact. In order to meet the nationally determined contribution (NDC) goals of the Korean industrial sector announced in 2021, our Green Management Vision 2030 aims to reduce GHG emissions by 14.5% compared to 2018.
To achieve the target, we establish and implement an annual facility investment plan for energy reduction, and all relevant departments, including planning, research, production, and power generation, formulate plans for mid- to long-term reduction goals and provide regular updates to the ESG Management Promotion Committee and the Board of Directors. Regarding reductions that are difficult to achieve through internal energy conservation efforts alone, we plan to promote long-term implementation through the purchase of domestic third-party PPAs produced with new and renewable energies and reduction certificates, and to gradually increase the use of renewable energy.
Execution strategy
-
1
GHG reduction through external reduction projects such as SDM* in line with the Paris Agreement
-
2
Reduction of GHG emissions through energy conservation measures at business sites and expansion of the use of new and renewable energies
-
3
Efficient GHG management facilitated by the in-house carbon asset management system and product carbon footprint calculation system
-
4
Establishment of a climate change risk and opportunity identification process for risk hedge and opportunity identification
* SDM(Sustainable Development Mechanism) 파리협정상의 지속가능개발체제
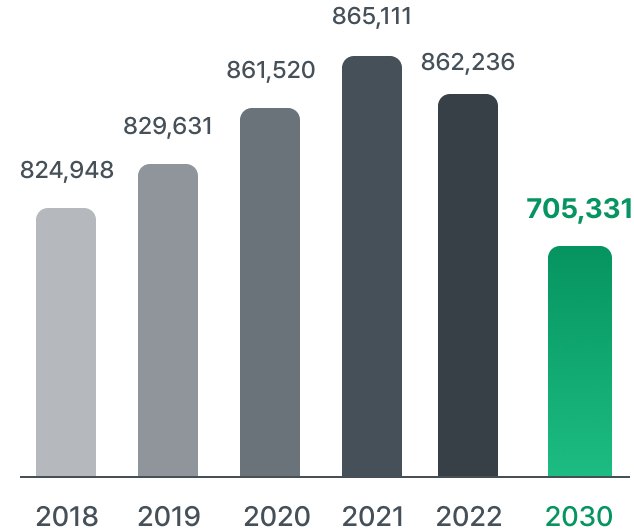
Carbon emission by year and 2030 goal
(Unit : tCO2eq)

Climate change risk management
Establishment and operation of management process
-
1
Stakeholder demands
-
2
Risk identification via analysis of the internal and external business environment
-
3
Severity rating
Hyosung Chemical has established a risk management process that can identify and systematically respond to climate change-related risks and opportunities. We identify and evaluate risks by analyzing stakeholder demands and the internal and external business environment. Climate change risk factors include transition risk due to market and technological changes resulting from the transition to a low-carbon economy, and short- and long-term physical risks due to the impact of climate change, such as typhoons, droughts, and floods.
Each year, Hyosung Chemical updates its risk management status in order to identify new risks and enhance the concreteness of its countermeasures. Significant risks are reported to the ESG Management Promotion Committee and assessed annually to determine if countermeasure objectives have been met. In addition, we have implemented internal carbon pricing1) to manage climate change risks and identify opportunities by incorporating them into strategic decision-making such as business direction and investment. We also use the carbon price according to GHG emissions for economic feasibility analysis when accounting for the cost of oversupply and deficit of emission allowances according to the emissions trading system, establishing workplace energy use plans, and making facility investments. This is done by calculating carbon emissions and distributing economic evaluation guidelines and GHG emission calculators throughout the organization.
1) Internal carbon price: A company voluntarily sets a price for carbon emissions to internalize the economic cost of GHG emissions.
Risk management process
Financial impact and response for climate change
and environmental issue risk/opportunity
| Risk / Opportunity | Period1) | Financial Impact2) | Response | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Risk |
Policy/ Regulation |
|
Mid to Long-term |
● |
|
|
| Technology |
|
Mid to Long-term |
- |
|
|
|
| Market |
|
Mid to Long-term |
● |
|
|
|
| Reputation |
|
Mid-term | - |
|
|
|
| Physical Risk |
Acute |
|
Short-term | ● |
|
|
| Chronic |
|
Long-term | - |
|
|
|
| Opportunity | Product /Service |
|
Mid to Long-term | ● |
|
|
| Market |
|
Short-term | ● |
|
|
|
1) Period: ① short-term: Within 1 year / ② Mid-term: Within 1 to 5 years / ③ Long-term: After 5 years
2) Financial Impact : High(●) more than KRW 1 billion/year, Medium (●) KRW 500 million to KRW 1 billion/year, Low (●) less than KRW 500 million/year.
-
Climate change indicator management
Carbon Asset Management System
Since 2011, Hyosung Chemical has implemented and operated an IT-based carbon asset management system to monitor emissions at each business site. Using the system, we establish a GHG inventory at each business site and ensure a systematic management by monitoring emissions by facility and activity data in accordance with the Emissions Calculation Plan. In addition, we implemented a system for calculating the carbon footprint of products in June 2022 so as to measure and manage carbon emissions throughout the product life cycle.
Carbon emissions management
Hyosung Chemical has set a quantitative goal to reduce GHG emissions by 14.5% by 2030 compared to 2018. To achieve this Green Management Vision 2030, we have predicted production yield, energy consumption, and GHG emissions by business site until 2030 based on the business plan and have established an annual reduction business plan. For reductions that are difficult to achieve through our reduction projects alone, mid- to long-term investments are required, such as the purchase of renewable energy certificates and the installation of new and renewable energy power generation facilities. We calculate the cost and determine the financial impact of these climate change risks based on internal carbon pricing.
Internal carbon price increase
In 2021, Hyosung Chemical introduced internal carbon pricing in order to identify risks and opportunities associated with climate change as a result of the transition to a low-carbon economy. We use this information for company-wide business direction and investment decisions. Internal carbon pricing entails the company voluntarily internalizing the economic cost of GHG emissions by establishing a price for carbon emitted from management and business activities. Accordingly, Hyosung Chemical converts both the amount of carbon emitted and the amount of carbon emissions cut resulting from energy savings into a monetary value, incorporates it into economic evaluation, and uses it for energy facility replacement, new business expansion, and business investment. We will continue to do all we can to reduce GHG emissions as part of our efforts to achieve the Vision 2030 objective.
Management of climate change-related employee key
performance indicators (KPIs) and incentivesAs performance indicators, Hyosung Chemical establishes energy reduction goals for production executives or plant managers relating to climate change, and GHG reduction goals for members of the Green Management Team. Their performances are evaluated so they are awarded incentives based on the evaluation outcomes. Moreover, in order to establish ESG management as a part of the corporate culture, the ESG Management Promotion Committee and the Board of Directors decided in 2021 to establish ESG management KPIs for employees and evaluate their performance. The initiative has been implemented since 2022. Accordingly, we have setup climate change indicators to evaluate all teams associated with energy conservation and greenhouse gas reduction, such as the ESG Management Team, Green Management Team, Production Team, and Power Generation Team, as well as relevant executives (including C-level).
-
Climate action
Development of eco-friendly materials using captured carbon dioxide
Hyosung Chemical promotes the development of an eco-friendly, low-carbon Poketone™ made from carbon monoxide produced by reforming carbon dioxide collected from factory effluent gas. We intend to continue to expand the commercialization of eco-friendly materials in an effort to reduce GHG emissions.
Expansion of renewable energy use
The Oksan, Yongyeon, and Gumi plants of Hyosung Chemical use waste heat to steam from incineration, a new and renewable energy source, from household waste incinerators near the business sites. The Yongyeon Plant uses the electricity generated by solar panels installed within the plant. Hyosung Chemical plans to continuously conduct solar panel installation projects at its business sites and to increase its use of new and renewable energies.
Building smart factories
Hyosung Chemical has set the establishment of smart factories as one of the Group's management policies and is continually improving its systems. In smart factories, all production-related resources are connected to the workplace in real-time, and the collected data is analyzed to build an optimized production environment. Enabling optimal operating conditions, smart factories not only contribute to increasing production yield but also reducing GHG emissions through lower energy consumption.
Support for energy conservation and GHG reduction for partners
Since signing business agreements for shared growth with large enterprises and SMEs with the Korea Energy Agency, Hyosung Chemical has been offering partners energy diagnosis and consulting services. Through a diagnosis of process and workplace environments, energy managers of partners can receive information on factors such as energy saving and GHG emission reduction factors, analysis of problems and economic feasibility, and improvement themes. We provide partners with support for energy-saving facilities where necessary.
Eco-friendly product and technology development
Hyosung Chemical focuses its efforts on the research and development of eco-friendly technologies and products, thereby securing future growth engines and achieving sustainable growth. We will take the lead in addressing climate change and establishing an eco-friendly business ecosystem through substantial investments in R&D, such as bolstering business capabilities for efficient energy use, setting up an eco-friendly hydrogen business, and developing resource recycling technology.
Learn more about Eco-friendly Technology Development
Task force activities for lowering carbon emissions
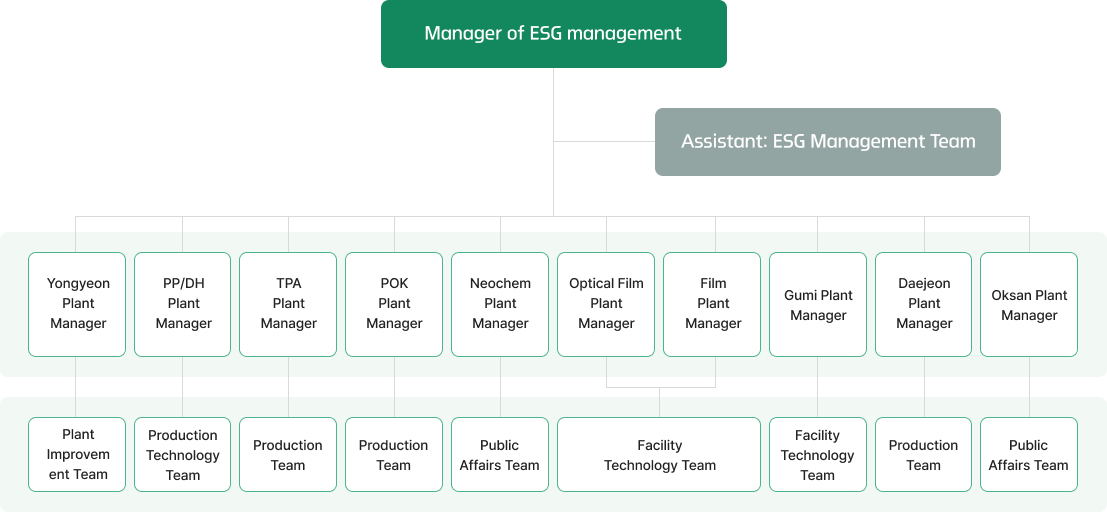
With carbon neutrality becoming an international concern, the national GHG emissions reduction target for 2030 in Korea has been increased. Hyosung Chemical has also increased its GHG emissions target to cut emissions by 14.5% by 2030 compared to 2018 levels. In an effort to reach our emissions target, we launched a carbon emissions reduction task force under the CEO. With the ESG Management Team leader, plant managers from each business unit and site, and the Public Affairs Team leader and Facility Technology Team leader as the members, the task force has formulated GHG reduction and energy-saving plans. Accordingly, we anticipate that the reduction strategy will be implemented with the highest impact.
|
Biodiversity activities
As the ecosystem continues to be destroyed by climate change, the obligation to preserve biodiversity is emerging. Hyosung Chemical supports and participates in efforts to preserve and promote biodiversity in order to nurture a thriving ecosystem for coming generations.
| Classification | Activity | Details | Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company-wide | Online training on climate change and biodiversity | Raising the awareness of biodiversity among employees | Every July |
| Each business site entitled to clean up a river | Habitat conservation such as removal of harmful plants | Ongoing | |
| Plogging alongside the Hangang River near Mapo-gu and Sebitseom | Plogging alongside the Hangang River near Mapo-gu and Sebitseom | Since 2022 | |
| Seagrass Forest Restoration Project | Threatened & Endangered Marine Species Restoration Project | 2023 (planned) | |
| Chemicals | Animal behavior enrichment | Support for the production and installation of animal feeding and movement-inducing devices | Since 2022 |
- Plogging: A portmanteau of the Swedish verb "plocka upp," which means "to pick up," and the English word "jogging." Plogging is the act of picking up trash while jogging or walking.